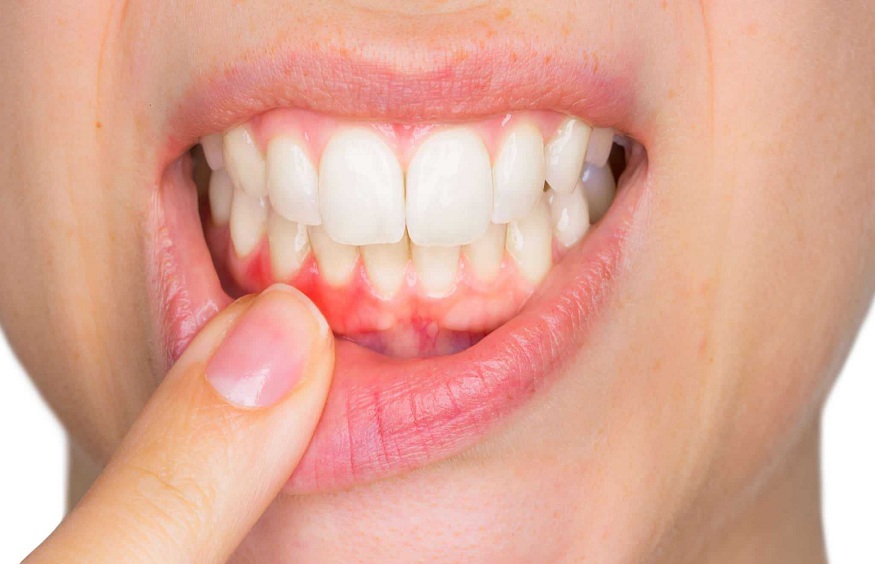
Gum recession is a progressive and potentially debilitating dental condition that can lead to tooth sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated. Seeking guidance from a reputable Whitby dentist is crucial in treating gum recession. Understanding the stages of gum recession is key to addressing this condition effectively.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the stages of gum recession, from mild gingivitis to severe gum recession, and provide valuable insights into treatment options, and proactive measures to maintain optimal gum health. By recognizing the early signs and symptoms, you can take control of your oral well-being and work with your Whitby dentist to develop a personalized plan for treating gum recession.
What is the Gum Recession?
Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, is a dental condition characterized by the progressive withdrawal of the gum tissue surrounding teeth, exposing the roots and increasing the risk of tooth decay, sensitivity, and tooth loss. It occurs when the gum tissue, which normally covers and protects the tooth roots, wears away or pulls back, revealing more of the tooth structure.
If left untreated, gum recession can compromise the stability and aesthetics of the smile, affecting overall oral health and self-confidence.
What Are The Stages of the Gum Recession?
Here is a detailed guide to the stages of gum recession:
Stage 1: Gingivitis (Mild Gum Recession)
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum recession, characterized by inflammation of the gums (gingiva). Symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
Treatment:
- Professional dental cleaning
- Improved oral hygiene habits
- Antibacterial mouthwash
Stage 2: Early Gum Recession (1-2 mm)
At this stage, the gum tissue starts to recede, exposing a small portion of the tooth root. Symptoms include:
- Slight tooth sensitivity
- Visible gum recession
- Pocket formation between teeth and gums
Treatment:
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Antibacterial therapy
- Gum grafting (optional)
Stage 3: Moderate Gum Recession (2-4 mm)
Gum recession progresses, exposing more of the tooth root. Symptoms include:
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Visible gaps between teeth and gums
- Loose teeth
Treatment:
- Gum grafting
- Bone grafting (if necessary)
- Dental restoration (crowns or fillings)
Stage 4: Advanced Gum Recession (4-6 mm)
At this stage, significant gum recession and bone loss occur, compromising tooth stability. Symptoms include:
- Severe tooth sensitivity
- Visible roots
- Tooth mobility
Treatment:
- Gum grafting
- Bone grafting
- Dental implants (if necessary)
- Periodontal surgery
Stage 5: Severe Gum Recession (Beyond 6 mm)
This stage is characterized by extensive gum recession, bone loss, and potential tooth loss. Symptoms include:
- Extreme tooth sensitivity
- Tooth loss
- Difficulty chewing or speaking
Treatment:
- Dental implants
- Bone grafting
- Periodontal surgery
- Prosthetic restoration
How is the Gum Recession Treated?
Gum recession treatment depends on the severity and underlying causes of the condition. Here are common treatment options:
Mild Gum Recession
- Professional dental cleaning (prophylaxis)
- Improved oral hygiene habits
- Antibacterial mouthwash
- Desensitizing toothpaste
Moderate Gum Recession
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Gum grafting (soft tissue graft)
- Bone grafting (if necessary)
- Antibacterial therapy
Severe Gum Recession
- Gum grafting (soft tissue graft)
- Bone grafting
- Dental restoration (crowns or fillings)
- Periodontal surgery
- Dental implants (if necessary)
Surgical Options
- Gum grafting: Transplanting healthy gum tissue to cover exposed roots.
- Bone grafting: Augmenting jawbone density to support teeth.
- Periodontal surgery: Reshaping gum tissue and bone to eliminate pockets.
- Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): Minimally invasive gum recession treatment.
Non-Surgical Options
- Laser treatment: Stimulating gum tissue regeneration.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Enhancing tissue healing.
- Antibacterial therapy: Controlling infection.
Gum recession is a progressive condition that can lead to severe consequences if left untreated. Understanding the stages of gum recession enables individuals to take proactive steps toward prevention and early detection. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene habits, and timely treatment can help prevent gum recession and ensure a healthy, beautiful smile.