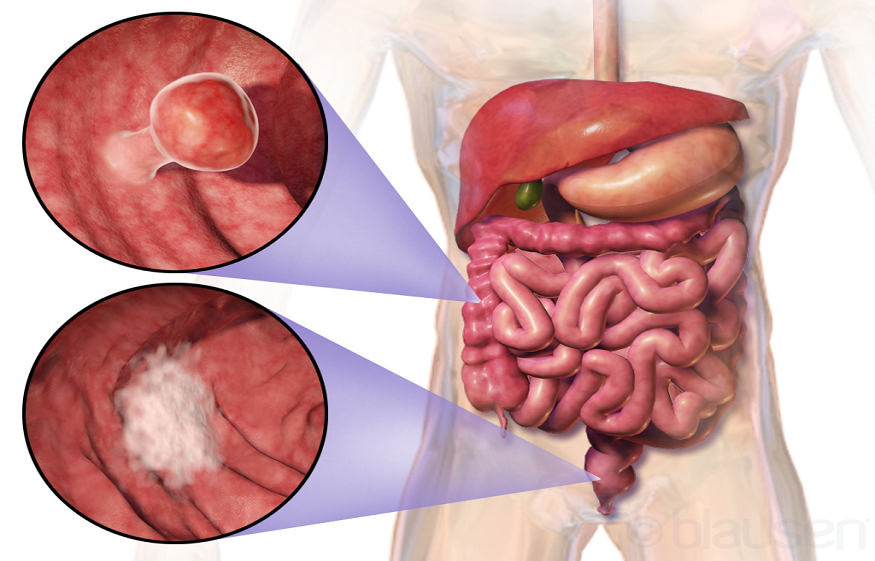
Food-related risk factors for colorectal cancer are the most studied, and therefore the best known risk factors for the disease. The scientific knowledge acquired on the preponderant role of diet in colorectal cancers has made it possible to determine how it could increase or decrease the risk of this cancer.
Today, research agrees on the fact that the consumption of red meat (especially beef), processed meat (by salting, smoking, etc.) and charcuterie increases the risk of colorectal cancer. It should not exceed 500 g of meat excluding poultry – which is however the case for 40% of men in France – and 150 g of charcuterie per week. It is estimated that in 2015, 5,600 cases of colorectal cancer could be attributed to the consumption of deli meats. More broadly, a diet high in calories, high in fat and low in fiber is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Conversely, the fibers contained in whole grains reduce the risk of colorectal cancer, as do dairy products, thanks to the calcium they contain. Finally, studies suggest that vegetables (non-starchy) and fruits, fish, foods containing vitamin C and foods containing vitamin D (oily fish, mushrooms, milk, etc.) would also have a protective effect.
Asbestos exposure
Several studies suggest an association between exposure to asbestos in the workplace and the occurrence of colorectal cancer, in particular colon cancer. The increased risk is greater if the exposure has lasted for many years 4
Overweight and obesity
The risk of colon cancer increases steadily from overweight (BMI greater than 25 kg/m 2 ). It rises even more in the event of obesity (BMI greater than 30 kg/m 2 ). It is understood that body fat content matters more than BMI, which can be high in athletes. The presence of abdominal adiposity (on the stomach) thus also increases the risk.
Sedentary lifestyle and physical activity
Sedentary behavior with long periods of sitting is also an established risk factor for colon cancer. Conversely, the practice of physical activity reduces the risk of colon cancer: up to 40 to 50% compared to sedentary people, depending on the regularity and intensity of the effort, an activity light already bringing benefits. A sedentary lifestyle or physical activity, however, does not seem to have an impact on rectal cancer.
Alcohol consumption and smoking
Alcohol consumption increases the risk of colorectal cancer from 2 drinks per day, in particular in men, and all the more so the longer it is. Wine, beer or strong alcohols are affected in the same way. Smoking moderately increases the risk of colorectal cancer, especially rectal cancer. The risk is higher in heavy smokers and long-time smokers.
Family and genetic factors
In 15% of cases, colorectal cancer appears on a predisposed family ground. The risk is higher when one or more first-degree relatives (father, mother, brother or sister) have been affected by the disease, especially before the age of 50. Colorectal cancers linked to a precisely identified genetic mutation represent 5% of cases.
Familial adenomatous polyposis, linked to the mutation of genes (APC, MUYTH) responsible for the appearance of hundreds, even thousands of colorectal polyps in adulthood. Without treatment for these polyps, the risk of colorectal cancer reaches 100%.
Lynch syndrome, or hereditary colon cancer without polyposis, is characterized by abnormalities in genes whose function is to correct mutations leading to the development of cancer: this is called microsatellite instability (MSI). The risk of colorectal cancer in those affected could be as high as 80%.